| |
Records |
Links |
|
Author |
Benner, S.G.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. |


|
| |
Title  |
A full-scale porous reactive wall for prevention of acid mine drainage |
Type |
Journal Article |
| |
Year |
1997 |
Publication |
Ground Water Monitoring and Remediation |
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
17 |
Issue |
4 |
Pages |
99-107 |
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage alkalinity bacteria Canada case studies concentration dissolved materials drainage Eastern Canada ground water mines observation wells Ontario permeability pH pollution porous materials recharge reduction remediation site exploration Sudbury District Ontario sulfate ion surface water waste disposal water pollution Groundwater quality Groundwater problems and environmental effects Pollution and waste management non radioactive geographical abstracts: physical geography hydrology (71 6 11) geomechanics abstracts: excavations (77 10 10) geological abstracts: environmental geology (72 14 2) groundwater protection permeable barrier acid mine drainage aquifer groundwater acid min drainage contamination permeable barrier groundwater protection permeable barrier acid mine drainage aquifer Canada, Ontario, Sudbury, Nickel Rim |
|
| |
Abstract |
The generation and release of acidic drainage containing high concentrations of dissolved metals from decommissioned mine wastes is an environmental problem of international scale. A potential solution to many acid drainage problem is the installation of permeable reactive walls into aquifers affected by drainage water derived from mine waste materials. A permeable reactive wall installed into an aquifer impacted by low-quality mine drainage waters was installed in August 1995 at the Nickel Rim mine site near Sudbury, Ontario. The reactive mixture, containing organic matter, was designed to promote bacterially mediated sulfate reduction and subsequent metal sulfide precipitation. The reactive wall is installed to an average depth of 12 feet (3.6 m) and is 49 feet (15 m) long perpendicular to ground water flow. The wall thickness (flow path length) is 13 feet (4 m). Initial results, collected nine months after installation, indicate that sulfate reduction and metal sulfide precipitation is occurring. Comparing water entering the wall to treated water existing the wall, sulfate concentrations decrease from 2400 to 4600 mg/L to 200 to 3600 mg/L; Fe concentration decrease from 250 to 1300 mg/L to 1.0 to 40 mg/L, pH increases from 5.8 to 7.0; and alkalinity (as CaCO<inf>3</inf>) increases from 0 to 50 mg/L to 600 to 2000 mg/L. The reactive wall has effectively removed the capacity of the ground water to generate acidity on discharge to the surface. Calculations based on comparison to previously run laboratory column experiments indicate that the reactive wall has potential to remain effective for at least 15 years. |
|
| |
Address |
Dr. S.G. Benner, Earth Sciences Department, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ont. N2L 3G1, Canada |
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
1069-3629 |
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Review; A full-scale porous reactive wall for prevention of acid mine drainage; 0337197; United-States 46; file:///C:/Dokumente%20und%20Einstellungen/Stefan/Eigene%20Dateien/Artikel/10621.pdf; Geobase |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 17555 |
Serial |
67 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Bienvenu, L. |

|
| |
Title  |
Activites de recherche du ministere des Ressources naturelles du Quebec sur le drainage minier acide; activites realisees dans le cadre de l'Entente auxiliaire Canada-Quebec 1992-1998 sur le developpement mineral; rapport 1993-1994. Research activities of Quebec Natural Resources Ministry on acid mine drainage; research related to the Canada-Quebec agreement 1992-1998 on mineral development; report 1993-1994 |
Type |
RPT |
| |
Year |
1994 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage; annual report; Canada; cost; Doyon Mine; Eastern Canada; methods; mining; mining geology; models; monitoring; organic compounds; organic materials; oxidation; permeability; pollution; programs; pyrite; Quebec; remediation; report; resins; sulfides; waste disposal; waste management; Weedon Mine 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
|
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Activites de recherche du ministere des Ressources naturelles du Quebec sur le drainage minier acide; activites realisees dans le cadre de l'Entente auxiliaire Canada-Quebec 1992-1998 sur le developpement mineral; rapport 1993-1994. Research activities of Quebec Natural Resources Ministry on acid mine drainage; research related to the Canada-Quebec agreement 1992-1998 on mineral development; report 1993-1994; 1995-039993; GeoRef; French; 18 tables Ministere des Ressources Naturelles, Charlesbourg, PQ, Canada |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 6520 |
Serial |
448 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Smyth, D.; Blowes, D.; Ptacek, C.; Bain, J. |


|
| |
Title  |
Application of permeable reactive barriers for treating mine drainage and dissolved metals in groundwater |
Type |
Journal Article |
| |
Year |
2004 |
Publication |
Geotechnical News |
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
22 |
Issue |
1 |
Pages |
39-44 |
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage; acid rock drainage; aquifers; Canada; Cochrane District Ontario; concentration; disposal barriers; Eastern Canada; ground water; Kidd Creek; mine drainage; mines; Ontario; oxidation; permeability; permeable reactive barrier; pollutants; pollution; remediation; sulfates; sulfides; tailings; testing; Timmins Ontario; waste disposal; waste management; waste rock; waste water; water treatment 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
|
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
0823-650x |
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Application of permeable reactive barriers for treating mine drainage and dissolved metals in groundwater; 2006-058196; References: 20; sects. Canada (CAN); GeoRef; English |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 5457 |
Serial |
66 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Berthelot, D.; Haggis, M. |
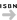

|
| |
Title  |
Application of remote monitoring and data management systems to environmental management of tailings facilities |
Type |
Book Chapter |
| |
Year |
1999 |
Publication |
Sudbury '99; Mining and the environment II; conference proceedings |
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage Algoma District Ontario applications Canada cost data management data processing Eastern Canada efficiency effluents Elliot Lake Ontario environmental analysis environmental management information management land management mining monitoring Ontario planning pollution remediation solid waste Stanleigh Mine tailings technology waste disposal 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
The mining industry has made tremendous strides in the last 20 years in the prevention and control of acid mine drainage. However, there remain a number of circumstances where the long-term operation, care and maintenance of tailings management facilities will be required. The application of progressive environmental technologies and management systems is key to cost control and environmental liability management at these sites. Mine Waste Management Inc. currently operates Rio Algom Limited's five effluent treatment plants and seven waste management areas in the Elliot Lake, Ontario region using a Remote Plant Monitoring and Control Network (RPMCN). This system, based on Intellutions's “Fix 32” technology, enables the monitoring and control of these plants from a centralized location thus reducing labour costs while providing 24-hour surveillance. Scheduling, auditing and reporting of plant operating and environmental monitoring programs are integrated and controlled using the Envista (super TM) environmental information management system. Proper application of these technologies and management systems facilitates delivery of cost-effective environmental monitoring, and care and maintenance programs at these sites and provides tools to demonstrate compliance with all environmental performance criteria. |
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
Goldsack, D.; Belzile, N.; Yearwood, P.; Hall, G. |
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
0886670470 |
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Application of remote monitoring and data management systems to environmental management of tailings facilities; GeoRef; English; 2002-060870; Sudbury '99; Mining and the environment II--Sudbury '99; L'exploitation miniere et l'environnement, Sudbury, ON, Canada, Sept. 13-17, 1999 References: 2; illus. incl. sketch map |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 16575 |
Serial |
449 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Zinck, J.M.; Aube, B.C. |

|
| |
Title  |
Optimization of lime treatment processes |
Type |
Journal Article |
| |
Year |
2000 |
Publication |
CIM Bull. |
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
93 |
Issue |
1043 |
Pages |
98-105 |
|
| |
Keywords |
Pollution and waste management non radioactive Groundwater problems and environmental effects geological abstracts: environmental geology (72 14 2) geomechanics abstracts: excavations (77 10 10) acid mine drainage buffering lime Canada |
|
| |
Abstract |
Lime neutralization technology is widely used in Canada for the treatment of acid mine drainage and other acidic effluents. In many locations, improvements to the lime neutralization process are necessary to achieve a maximum level of sludge densification and stability. Conventional lime neutralization technology effectively removes dissolved metals to below regulated limits. However, the metal hydroxide and gypsum sludge generated is voluminous and often contains less than 5% solids. Despite recent improvements in the lime neutralization technology, each year, more than 6 700 000 m3 of sludge are generated by treatment facilities operated by the Canadian mining industry. Because lime neutralization is still seen as the best available approach for some sites, sludge production and stability are expected to remain as issues in the near future. Several treatment parameters significantly impact operating costs, effluent quality, sludge production and the geochemical stability of the sludge. Studies conducted both at CANMET and NTC have shown that through minor modifications to the treatment process, plant operators can experience a reduction in operating costs, volume of sludge generated, metal release to the environment and liability. This paper discusses how modifications in plant operation and design can reduce treatment costs and liability associated with lime treatment. |
|
| |
Address |
J.M. Zinck, CANMET, Mining and Mineral Sciences Lab., Natural Resources Canada, Ottawa, Ont., Canada |
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
0317-0926 |
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Optimization of lime treatment processes; 2291672; Canada 17; Geobase |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 17537 |
Serial |
183 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |

