| |
Records |
Links |
|
Author |
Anonymous |

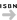

|
| |
Title |
|
Type |
Book Whole |
| |
Year |
1998 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
118 pp |
|
| |
Keywords |
abandoned mines; acid mine drainage; aquifer vulnerability; aquifers; arsenic; bibliography; bioremediation; chemical properties; chemical waste; chromium; constructed wetlands; decontamination; disposal barriers; ground water; grouting; industrial waste; metals; microorganisms; mines; mobility; phytoremediation; pollutants; pollution; programs; reclamation; remediation; sludge; soil treatment; soils; solvents; sorption; Superfund; surface water; tailings; toxic materials; waste disposal; waste disposal sites; water quality; wetlands 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
|
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration |
Place of Publication |
Littleton |
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
Remediation of historical mine sites; technical summaries and bibliography |
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
0873351622 |
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Remediation of historical mine sites; technical summaries and bibliography; 1998-031431; GeoRef; English |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 6164 |
Serial |
11 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Anonymous; Unten, L.; Wildeman, T.R.; Gusek, J.J. |
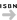

|
| |
Title |
Passive treatment for contaminants in mine waters Effluent treatment in the mining industry |
Type |
Book Chapter |
| |
Year |
1998 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage; alkalinity; biodegradation; chemical reactions; coal mines; constructed wetlands; controls; degradation; heavy metals; ions; kinetics; metal ores; mines; mitigation; oxidation; pH; pollution; polymetallic ores; remediation; solubility; sulfate ion; sulfides; waste disposal; wetlands 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
|
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
University of Concepcion |
Place of Publication |
Concepcion |
Editor |
Castro, S.H.; Vergara, F.; Sanchez, M.A. |
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
University of Concepcion, D. of M.E.C.C. |
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
9562271560 |
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Passive treatment for contaminants in mine waters Effluent treatment in the mining industry; GeoRef; English; 2002-047084; References: 59; illus. incl. 3 tables |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 6215 |
Serial |
477 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Arango, I. |

|
| |
Title |
Evaluation of the beneficial effects of the acidophilic alga Euglena mutabilis on acid mine drainage systems |
Type |
Book Whole |
| |
Year |
2002 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage atmospheric precipitation benthic taxa bioremediation dissolved materials dissolved oxygen electron microscopy data Euglena mutabilis Green Valley Mine ICP mass spectra Indiana iron mass spectra metals microorganisms mines oxygen pH photochemistry photosynthesis pollution rain remediation sediments soils spectra temperature United States Vigo County Indiana water 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
Euglena mutabilis is an acidophilic, photosynthetic protozoan that forms benthic mats in acid mine drainage (AMD) channels. At the Green Valley mine, western Indiana, E. mutabilis resides in AMD measuring <4.2 pH, with high concentrations of dissolved constituents (up to 22.67 g/l). One of the main factors influencing E. mutabilis distribution is water temperature. The microbe forms thick (>1 mm), extensive mats during spring and fall, when water temperature is between 13 and 28 degrees C. During winter and summer, when temperatures are outside this range, benthic communities have a very patchy distribution and are restricted to areas protected from extreme temperature changes. E. mutabilis also responds to rapid increases in pH, which are associated with rainfall events. During these events pH can increase above 4.0, causing precipitation of Fe and Al oxy-hydroxides that cover the mats. The microbe responds by moving through the precipitates, due to phototaxis, and reestablishing the community at the sediment-water interface within 12 hours. The biological activities of E. mutabilis may have a beneficial effect on AMD systems by removing iron from effluent via oxygenic photosynthesis, and/or by internal sequestration. Photosynthesis by E. mutabilis contributes elevated concentrations of dissolved oxygen (DO), up to 17.25 mg/l in the field and up to 11.83 mg/l in the laboratory, driving oxidation and precipitation of reduced metal species, especially Fe (II), which are dissolved in the effluent. In addition, preliminary electro-microscopic and staining analyses of the reddish intracellular granules in E. mutabilis indicate that the granules contain iron, suggesting that E. mutabilis sequesters iron from AMD. Inductive coupled plasma analysis of iron concentration in AMD with and without E. mutabilis also shows that E. mutabilis accelerates the rate of Fe removal from the media. Whether iron removal is accelerated by internal sequestration of iron and/or by precipitation via oxygenic photosynthesis has yet to be determined. These biological activities may play an important role in the natural remediation of AMD systems. |
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
Ph.D. thesis |
|
| |
Publisher |
Indiana State University, |
Place of Publication |
Terre Haute |
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
|
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
Evaluation of the beneficial effects of the acidophilic alga Euglena mutabilis on acid mine drainage systems; GeoRef; English; References: 39; illus. incl. 3 tables |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 16491 |
Serial |
476 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Ashby, J.C. |

|
| |
Title |
Injecting alkaline lime sludge and FGD material into underground mines for acid abatement |
Type |
Journal Article |
| |
Year |
2001 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage; air quality; alkalinity; chemical composition; coal; combustion; discharge; energy sources; gaseous phase; industrial waste; monitoring; pollution; power plants; regulations; remediation; sedimentary rocks; soils; tailings ponds; toxicity; waste disposal 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
|
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
West Virginia Surface Mine Drainage Task Force Symposium |
Place of Publication |
|
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
Proceedings, 22nd West Virginia surface mine drainage task force symposium |
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
2002-047119; Twenty-second West Virginia surface mine drainage task force symposium, Morgantown, WV, United States, April 3-4, 2001 References: 5; illus. incl. 3 tables; GeoRef; English |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 5763 |
Serial |
475 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |
| |
|
| |
|
Author |
Aube, B.C.; Zinck, J.M. |

|
| |
Title |
Comparison of AMD treatment processes and their impact on sludge characteristics |
Type |
Journal Article |
| |
Year |
1999 |
Publication |
|
Abbreviated Journal |
|
|
| |
Volume |
|
Issue |
|
Pages |
|
|
| |
Keywords |
acid mine drainage cost decontamination density discharge geochemistry hydrochemistry leaching lime metals mine dewatering neutralization pH pollution remediation sludge stability tailings toxicity viscosity waste disposal water treatment 22, Environmental geology |
|
| |
Abstract |
Lime neutralisation for the treatment of acid mine drainage is one of the oldest water pollution control techniques practised by the mineral industry. Several advances have been made in the process in the last thirty years, particularly with respect to discharge concentrations and sludge density. However, the impact of different treatment processes on metal leachability and sludge handling properties has not been investigated. A study of treatment sludges sampled from various water treatment plants has shown that substantial differences can be related to the treatment process and raw water composition. This study suggests that sludge densities, excess alkalinity, long-term compaction properties, metal leachability, crystallinity and cost efficiency can be affected by the neutralisation process and specific process parameters. The study also showed that the sludge density and dewatering ability is not positively correlated with particle size as previously suggested in numerous studies. The treatment process comparisons include sludge samples from basic lime treatment, the conventional High Density Sludge (HDS) Process, and the Geco HDS Process. |
|
| |
Address |
|
|
| |
Corporate Author |
|
Thesis |
|
|
| |
Publisher |
|
Place of Publication |
Sudbury |
Editor |
|
|
| |
Language |
|
Summary Language |
|
Original Title |
|
|
| |
Series Editor |
|
Series Title |
Mining and the Environment II |
Abbreviated Series Title |
|
|
| |
Series Volume |
|
Series Issue |
|
Edition |
|
|
| |
ISSN |
|
ISBN |
|
Medium |
|
|
| |
Area |
|
Expedition |
|
Conference |
|
|
| |
Notes |
2002-060865; Sudbury '99; Mining and the environment II--Sudbury '99; L'exploitation miniere et l'environnement, Sudbury, ON, Canada, Sept. 13-17, 1999 References: 10; illus. incl. 6 tables; GeoRef; English |
Approved |
no |
|
| |
Call Number |
CBU @ c.wolke @ 16574 |
Serial |
473 |
|
| Permanent link to this record |

