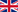
Conversion factors for Redox Probes
Prof. Dr. Christian Wolkersdorfer
Calculation of the Redoxpotential from the Reading of the ORP-Probe (“Redox Compensation”)
Measuring the redox potential of an aqueous solution is essential to understand the conditions within that solution. Yet, redox probes usually do not show the redox potential of the solution as a reference to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), but as the potential of the probe in relation to the solution. For a first estimation of the redox-potential of the solution, adding +200 mV to the reading of the probe gives a close value of the real situation. Yet, for a detailed study, the redox potential needs to be calculated form the reading and the temperature of the solution. In most cases, this is done by using a two-step-approach: first the temperature compensation and then the redox compensation using two tables or nonograms. Yet, the procedure can substantially be simplified by using an equation, as published by Wolkersdorfer (2008). This equation uses the solution’s temperature T [°C] and the ORP reading of the electrode Et [mV] as well as the Nernst-Equation and two constants a and b to calculate the redox potential relative to the SHE:
E0(25°C) = Et – 0.198 × (T - 25) + √(a – b × T) [equation 1]
Let’s assume an “Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3 mol/L“ redox electrode was used and a temperature of 11.5 °C and an ORP reading of 194 mV obtained. The above equation 1 then becomes:
E0(25°C) = 194 – 0.198 × (11.5 – 25) + √(50301 – 297 × 11.5) mV =
194 + 2.673 + 216.531 mV = 413 mV (410 mV according to DIN 38404-6)
Here you can find my pH average calculator
Online Calculator
© Christian Wolkersdorfer 2017– (V 1.3 20210610)
| Electrode type | a | b |
|---|---|---|
| “Silberchlorid”, “Argenthal”, “Silamid” Ag/AgCl, KCl, 1 mol/L | 62755 | 284 |
| “Silberchlorid”, “Argenthal”, “Silamid” Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3 mol/L | 50301 | 297 |
| “Silberchlorid”, “Argenthal”, “Silamid” Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3.5 mol/L | 49083 | 310 |
| “Silberchlorid”, “Argenthal”, “Silamid” Ag/AgCl, KCl, saturated | 47591 | 356 |
| “Calomel” Hg/Hg₂C₂, KCl, 0.1 mol/L | 112238 | 58 |
| “Calomel” Hg/Hg₂C₂, KCl, 1 mol/L | 82571 | 183 |
| “Calomel” Hg/Hg₂C₂, KCl, saturated | 67798 | 324 |
| “Thalamid” Tl, Hg/TlCl, KCl, 3,5 mol/L | – | – |
| “Quecksilbersulfat” Hg/Hg₂SO₄, K₂SO₄, saturated | 451702 | 1.090 |
| Ag/AgCl, KCl, 4 mol/L | 56544 | 287 |
| Hanna Ag/AgCl, KCl, 1 mol/L | 69791 | 196 |
| Hanna Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3 mol/L | 49296 | 298 |
| Hanna Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3.5 mol/L | 50301 | 297 |
| Hanna Ag/AgCl, KCl, saturated | 49655 | 401 |
| Hach Ag/AgCl, KCl, 3 mol/L | 50301 | 297 |
| WTW SenTix ORP Ag/AgCl 3 KCl mol/L, Au | 50301 | 297 |
| WTW SenTix PtR | 47591 | 356 |
| DIN Ag/AgCl/KCl, 1 mol/L (DIN correction 1: 2018-06-29) | 62647 | 277 |
| DIN Ag/AgCl/KCl, 3 mol/L (DIN correction 1: 2018-06-29) | 50239 | 298 |
| DIN Ag/AgCl/KCl, 3.5 mol/L (DIN correction 1: 2018-06-29) | 49525 | 328 |
| DIN Ag/AgCl/KCl, saturated (DIN correction 1: 2018-06-29) | 48852 | 404 |
| Troll 9500 | 46230 | 328 |
| Knick SE 564, SE 554, SE 565 | 50301 | 297 |
Equation provides redox values with an error of ± 5 mV between 5 and 65 °C. The online calculator uses up to 7 decimal places.